Confused about retinol vs retinoid? These two skincare terms get mixed up all the time, leaving people wondering which one they should actually use.
The truth is, they’re related but not identical, and knowing the difference can help you pick the right product for your skin goals.
Retinoids are vitamin A derivatives that fight wrinkles, acne, and dark spots, while retinol is just one type within that family.
Some are gentle enough for drugstore shelves, while others need a doctor’s prescription. Understanding retinol vs retinoid will save you money, time, and potential skin irritation as you build your perfect skincare routine.
Is Retinol a Retinoid? Understanding the Basics
Many people wonder if retinol and retinoids are the same thing. Here’s the simple answer: retinoid is like a family name for all vitamin A derivatives used in skincare. Retinol is just one member of that family.
Think of it like how “fruit” includes apples, oranges, and bananas – retinoids include retinol, retinaldehyde, and prescription tretinoin.
The confusion happens because people often use these terms interchangeably, but they’re not exactly the same.
Retinol is always a retinoid, but not all retinoids are retinol. Understanding this difference helps you make better choices when shopping for anti-aging products and talking to your dermatologist.
Retinoic Acid vs Retinol: What’s the Real Difference?
Your skin can’t actually use retinol directly. It needs to convert retinol into retinoic acid first, which is the only form your skin cells recognize and respond to.
This conversion occurs in two steps: retinol is converted to retinaldehyde, and retinaldehyde is converted to retinoic acid. Each conversion takes time and reduces the strength.
That’s why retinol is gentler than prescription retinoic acid (tretinoin), which goes straight to work without needing conversion. The trade-off is simple – retinol causes less irritation but takes longer to show results.
Retinoic acid works faster but can be harsh on sensitive skin, which is why it requires a prescription.
The Benefits of Retinol and Retinoids for Your Skin
Both retinol and retinoids offer amazing benefits for your skin, but they work at different strength levels.
Understanding what each one can do helps you pick the right option for your needs.
Retinol
Retinol is a popular over-the-counter option that works well for most people starting their anti-aging routine. It’s gentle enough for regular use while still delivering visible results over time.
- Reduces fine lines and wrinkles by boosting collagen production in your skin
- Fades dark spots and evens out skin tone for a brighter complexion
- Unclogs pores and helps control breakouts, making it useful for acne-prone skin
- Improves overall skin texture, making it smoother and more refined
Retinol is perfect for beginners because it’s less likely to cause redness or peeling compared to stronger options. You can find it in many drugstore and beauty counter products without needing a prescription.
Retinoids
Prescription retinoids are more powerful and work faster than over-the-counter retinol. Dermatologists often recommend them for specific skin concerns that need stronger treatment.
- Treats moderate to severe acne more effectively than gentler alternatives
- Speeds up cell turnover to reveal fresher, younger-looking skin quickly
- Significantly reduces deep wrinkles and signs of sun damage
- Works well for stubborn hyperpigmentation and melasma that doesn’t respond to milder products
While retinoids deliver stronger results, they require careful use and may cause initial irritation as your skin adjusts. Always talk to your dermatologist to see if a prescription retinoid is right for your skin type.
How to Choose Between Retinol and Retinoids?
Choosing between retinol and retinoids depends on your skin type and concerns. If you have sensitive skin or you’re new to vitamin A products, start with a low-strength retinol (0.25% to 0.5%).
This gives your skin time to adjust without major irritation. For stubborn acne, deep wrinkles, or severe sun damage, prescription retinoids work better and faster.
Common side effects include redness, dryness, and peeling during the first few weeks.
Build tolerance by using the product twice weekly at first, then slowly increase to nightly use. Always apply sunscreen during the day since retinoids make your skin more sensitive to sun damage.
Product Recommendations for Retinol and Retinoids
Choosing the right product depends on your skin type and goals. The Ordinary Retinol 0.5% in Squalane is great for beginners and sensitive skin, offering gentle hydration and good absorption.
For anti-aging, Neutrogena Rapid Wrinkle Repair Regenerating Cream with retinol SA works well for most skin types. RoC Retinol Correxion Deep Wrinkle Night Cream helps reduce fine lines with minimized irritation.
For stronger options, Tretinoin (Retin-A Micro) is a powerful prescription retinoid used for acne and aging, requiring dermatologist supervision.
Adapalene Differin Gel is a gentler prescription retinoid effective for acne and long-term skin health.
Tips for Using Retinol and Retinoids Safely and Effectively
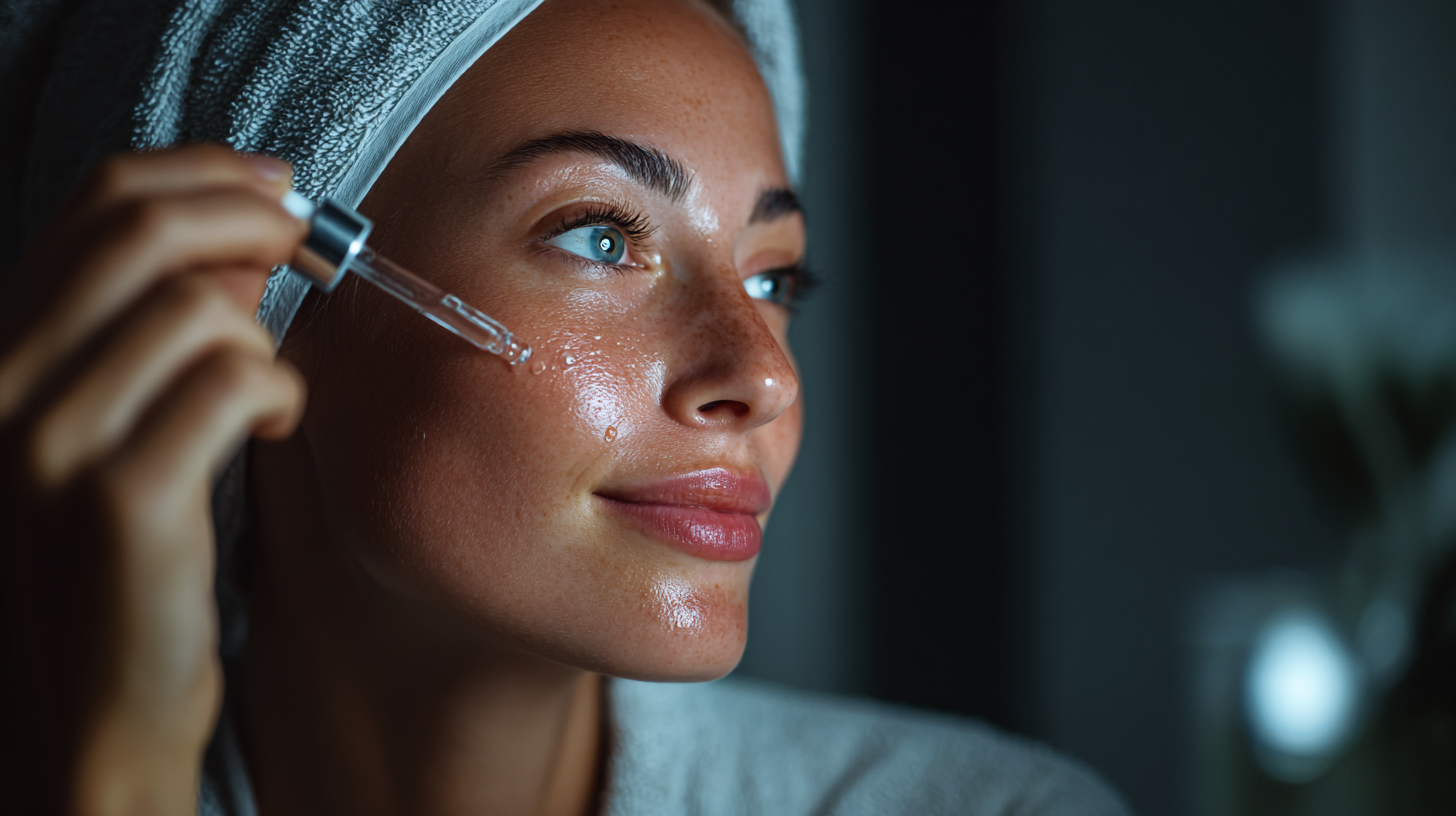

Using retinol or retinoids correctly makes a big difference in getting good results without irritating your skin. Following these basic tips will help you avoid common mistakes and see the best improvements.
- Apply only at night, since sunlight breaks down the ingredients.
- Use a pea-sized amount for your entire face.
- Wait until skin is completely dry after cleansing before applying.
- Layer moisturizer on top to reduce dryness.
- Wear sunscreen every morning to protect sensitive skin.
Patience is important when using these products since results typically take 8 to 12 weeks to become noticeable. Stick with your routine and avoid mixing retinoids with harsh exfoliants like acids or scrubs in the beginning.
That’s a Wrap
Now you know the real story behind retinol vs retinoid and how to choose the best option for your skin.
Remember, retinol works great for beginners and everyday use, while stronger retinoids tackle stubborn concerns faster with a prescription. Start slow, be patient, and always protect your skin with sunscreen.
Consistent use over time brings the best results. Have you tried retinol or retinoids before?
Drop a comment below sharing your experience – did you notice a difference in your skin? What strength worked best for you? Your story might help someone else make the right choice for their skincare routine.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can Retinol Cause Skin Irritation?
Yes, but it is generally gentler than prescription retinoids and causes less redness or peeling.
Are Retinoids Suitable For Sensitive Skin?
They can be, but lower-strength options or gradual introduction are recommended.
Can I Use Retinol And Retinoids During The Day?
No, they should only be applied at night to prevent sun damage.
Can Retinoids Treat Acne And Wrinkles?
Yes, they are effective for acne, deep wrinkles, and stubborn hyperpigmentation.







